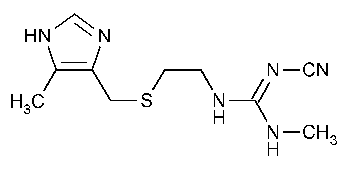
Hydrochloric acid is produced in stomach to bring out the digestion process. But excess production of acid leads to acidity. Sometimes it may also lead to ulcers in the stomach. Earlier sodium hydrogen carbonate is used to treat acidity. Metal hydroxides are more preferred because of being insoluble and do not increase the pH above neutrality. Studies have reported that Histamine stimulates the release of pepsin and hydrochloric acid in stomach. A drug known as cimetidine prevents the interaction between histamine and the receptors in the stomach. This decreases the amount of released histamine. Later on, another drug came into the market which is known as ranitidine. This drug is still common among the people.
Fig. 1. Structure of Cimetidine
Antihistamines
Histamine is a vasodilator. It contracts the smooth muscles of the gut and the bronchi. Drugs such as brompheniramine (Dimetapp) and terfenadine (Seldane), act as antihistamines. These drugs compete with histamine for binding site on the receptors.
Neurologically Active Drugs
Tranquilizers
These are drugs used to treat stress, or other mental diseases. They also act as sleeping pills. There are different types of tranquilizers. For Example, noradrenaline plays an important role in mood changes. During low level of noradrenaline, person suffers from depression. For this situation, antidepressants are taken. Antidepressants inhibits enzymes that degrades noradrenaline.
Some tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide is mild tranquilizer. Equanil is another tranquilizer which is used for controlling depression and hypertension.
Fig. 2. Structure of Equanil
Analgesic
These drugs are used to treat pain without causing any mental illness. Analgesics are classified into- non-narcotic analgesic and narcotic analgesic.
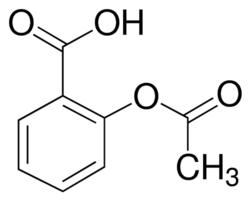
Non-narcotic analgesic such as aspirin acts as inhibitor of prostaglandins. These drugs are also used to treat pain of arthritis. Analgesics are also used to reduce fever. Such drugs are known as Antipyretic.
Fig. 3. Structure of Aspirin
Narcotic analgesic is used to relieve pain and give a feeling of sleepiness. For Example, morphine. Excess dose of morphine may cause convulsions, coma, or even death.
Antimicrobials
Antimicrobials includes bacteria, viruses, fungi etc. it includes:
Antibiotic
These are used to treat infections caused by pathogens. Antibiotics in low dose inhibits the growth of the microorganisms. But these also inhibits the activity of beneficial bacteria. Some antibiotics kills the microorganisms, they are known as Bactericidal. For Example, Penicillin.
Some inhibits the microorganisms instead of killing them. Such drugs are known as Bacteriostatic. For Example, erythromycin, tetracycline.
Some antibiotics target only limited range of microorganisms, they are known as Narrow Spectrum Antibiotics. For Example, Penicillin G. But some target wide range of microorganisms, they are known as Broad Spectrum Antibiotic. For Example, Ampicillin.
Fig. 4. Structure of Ampicillin
Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and disinfectants also acts on microorganisms to kill or inhibit them. Antiseptics acts on living tissues. Such as Soframicine. They are not consumed orally, rather they are applied on infected area. Dettol is one of the commonly used antiseptics. It is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol. Iodine also acts as powerful antiseptic.
Disinfectants are used on non-living objects such as drainage system, floors etc.1% solution of phenol acts as disinfectant.
Antifertility Drugs
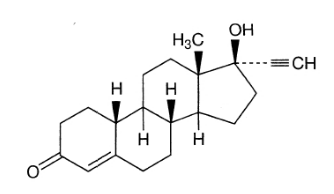
These drugs are used to control the population. They are commonly known as Birth Control Pills. These drugs are composed of synthetic hormones. Norethindrone is an antifertility drug
Fig. 5. Structure of Norethindrone
which is a derivative of progesterone. Ethynylestradiol (novestrol) is an estrogen derivative which is used in combination with progesterone derivative.
Positive and Negative Effects of Drugs
Positive effects of drugs
•They cure diseases!
Drugs have numerous positive effects. In fact, all of our medicines are drugs. Cancers and other fatal diseases were impossible to cure before the discovery of drugs like taxol and cisplatin. The wonders drugs have done in the world of medication is indescribable in a few words.
• They make pain bearable.
Drugs having a sedative effect often help patients cope with nail-biting pain and assist doctors to carry on surgical procedures. Pain-killers are a huge discovery that is, until today, the sole basis of ease to patients. Aspirin cures headaches and is a wonder in the case of inflammation.
•They create research and job opportunities
With the rise in drug intake, more and more manufacturing companies are coming up with hundreds of job opportunities. Research scientists are also always on the lookout to find something better than what exists.
• Helps people escape reality
One cannot argue, legal or not, drugs are the best way to escape reality and have a little relaxation period. Along with being a stress buster, it has also been proven to be a performance enhancer. Once on drugs, some people have reported a heightened view of the world as a glorious place. Your mood, creativity, confidence, self-confidence, and perception of life can reach a whole new level with correct administration of drugs.
Negative effects of drugs
•Drug abuse
Drug abuse refers to the point where a person starts taking drugs without a physician’s guidance and in order to experience pleasure. As drugs induce a feeling of getting “high”, drug abuse is a very common problem today. It has ended in fatality for many unfortunate souls.
• Addiction
Followed by drug abuse, people start getting addicted to drugs. It isn’t uncommon, really! The levels of dopamine released when we take drugs are enough to make our body crave for more. If we give in to the cravings, we are gone – life starts having a singular meaning, “drugs”. As we know, all sorts of addictions are bad for health, so are drugs!
• Legal problems
Often, drugs that are consumed for pleasure are illegal. Also, consumption of drugs is prohibited in many workplaces. Driving and roaming in public under the influence of drugs can also lead to legal action.
• Side effects
Many times, even after a physician’s guidance, drugs may lead to adverse side effects. After all, drugs are chemical substances and not natural. When chemicals infuse with our body, they may spark mutations and problems that may cause various diseases and other problems.
• Money wastage
When addicted, drugs can lead you to money wastage. You start investing all your money and time into drugs. It’s a vicious cycle that never ends. You start going down in debts and losing everything. Your work, home, and health start getting affected – to stabilize which you invest even more money!
[copied]